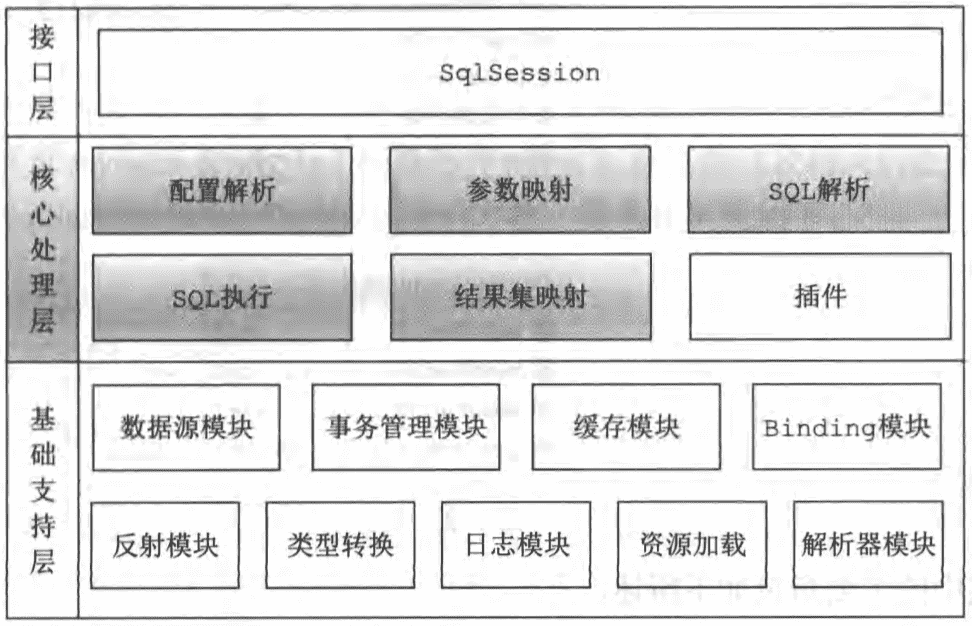
核心处理层以基础支持层为基础,实现了MyBatis的核心功能。这个部分将从MyBatis的初始化、动态SQL语句的解析、结果集的映射、参数解析以及SQL语句的执行等几个方面分析MyBatis的核心处理层,了解MyBatis的核心原理。
本篇介绍MyBatis的初始化
在MyBatis初始化的过程中,除了会读取mybatis-config.xml配置文件以及映射配置文件,还会加载配置文件指定的类,处理类中的注解,创建一些配置对象,最终完成框架中各个模块的初始化。
另外,也可以使用JavaAPI的方式对MyBatis进行配置,这种硬编码的配置方式主要用在配置量比较少且配置信息不常变化的场景下。
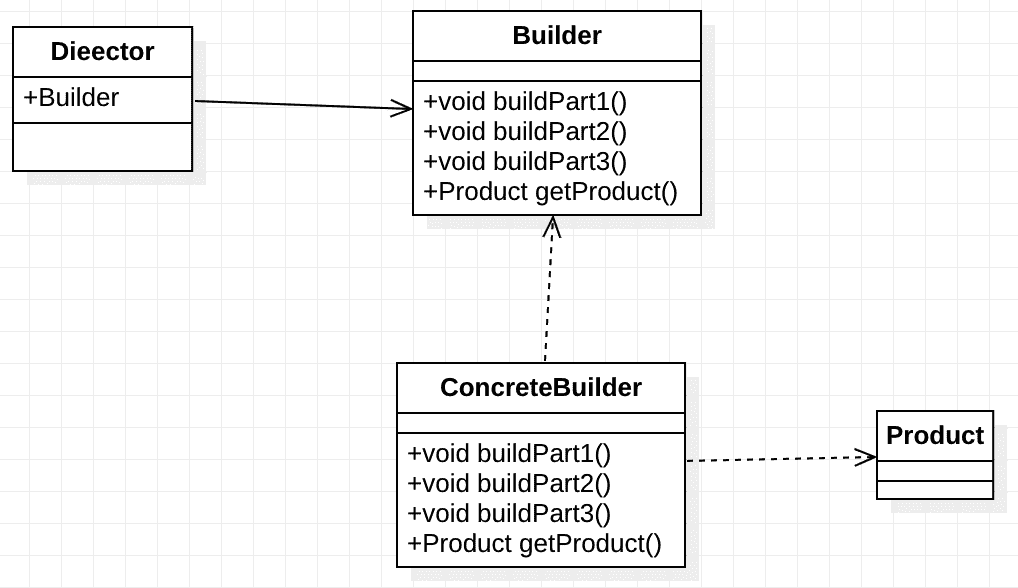
建造者模式 在MyBatis处理mybatis-config.xml以及映射配置文件时,会在内存中创建相应的配置对象,该过程的设计使用到建造者模式 的相关知识。
建造者模式中的主要角色如下:
建造者(Builder)接口
Builder接口用于定义建造者构建产品对象的各部分的行为。
具体建造者(ConcreteBuilder)角色
在建造者模式中,直接创建产品对象的是具体建造者。 具体建造者类必须实现建造者接口所要求的两类方法:
一类是建造方法,如上图中的buildPart1()、buildPart2()等方法。
另一类是获取构建好的产品对象的方法,如上图中的getProduct()方法。
导演(Director)角色
该角色会通过调用具体建造者, 创建需要的产品对象
产品(Product)角色
产品对象就是用户需要使用的复杂对象
建造者模式的优点:
建造者模式中的导演角色并不需要知晓产品类的内部细节,它只提供需要的信息给建造者,由具体建造者处理这些信息(这个处理过程可能会比较复杂)并完成产品构造。这就使产品对象的上层代码与产品对象的创建过程解耦。
建造者模式将复杂产品的创建过程分散到了不同的构造步骤中,这样可以对产品创建过程实现更加精细的控制,也会使创建过程更加清晰。
每个具体建造者都可以创建出完整的产品对象,而且具体建造者之间是相互独立的,因此系统就可以通过不同的具体建造者,得到不同的产品对象。当有新产品出现时,无须修改原有的代码,只需要添加新的具体建造者即可完成扩展 ,这符合开放-封闭 原则。
建造者模式也有一些缺点,它所创建的产品一般具有较多的共同点,其组成部分相似,如果产品之间的差异性很大,则不适合使用建造者模式。
如果产品种类较多,且内部变化复杂,就需要定义多个具体建造者类来实现这种变化,导致整个系统变得很复杂,不易于理解。
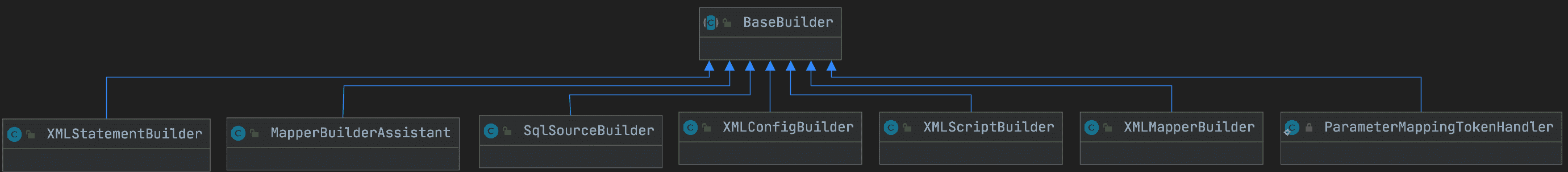
BaseBuilder MyBatis初始化的主要工作是加载并解析mybatis-config.xml配置文件、映射配置文件以及相关的注解信息。MyBatis的初始化入口是SqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build()方法,其具体实现如下:
public SqlSessionFactory build (Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) { try { XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder (reader, environment, properties); return build(parser.parse()); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession." , e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { } } }
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build()方法会创建XMLConfigBuilder对象来解析mybatis-config.xml配置文件,而XMLConfigBuilder继承自BaseBuilder抽象类。
MyBatis的初始化过程使用了建造者模式,这里的BaseBuilder抽象类就扮演着建造者接口的角色。BaseBuilder中核心字段的含义如下:
protected final Configuration configuration;protected final TypeAliasRegistry typeAliasRegistry;protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry;
BaseBuilder中记录的TypeAliasRegistry对象和TypeHandlerRegistry对象,其实是全局唯一的,它们都是在Configuration对象初始化时创建的。
Configuration类中定义了这两个字段:
protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = new TypeHandlerRegistry ();protected final TypeAliasRegistry typeAliasRegistry = new TypeAliasRegistry ();
在BaseBuilder构造函数中,通过相应的Configuration.get*()方法得到TypeAliasRegistry对象和TypeHandlerRegistry对象,并赋值给BaseBuilder相应字段。
BaseBuilder.resolveAlias()方法依赖TypeAliasRegistry解析别名,BaseBuilder.resolveTypeHandler()方法依赖TypeHandlerRegistry查找指定的TypeHandler对象。
MyBatis使用JdbcType枚举类型表示JDBC类型。MyBatis中常用的枚举类型还有ResultSetType和ParameterMode:ResultSetType枚举类型表示结果集类型,使用ParameterMode枚举类型表示存储过程中的参数类型。
在BaseBuilder中提供了相应的resolveJdbcType()、resolveResultSetType()、resolveParameterMode()方法,将String转换成对应的枚举对象。
XMLConfigBuilder XMLConfigBuilder是BaseBuilder的众多子类之一,它扮演的是具体建造者的角色。**XMLConfigBuilder主要负责解析mybatis-config.xml配置。**
核心字段:
private boolean parsed;private final XPathParser parser;private String environment;private final ReflectorFactory localReflectorFactory = new DefaultReflectorFactory ();
XMLConfigBuilder.parse()方法是解析mybatis-config.xml配置文件的入口,它通过调用XMLConfigBuilder.parseConfiguration()方法实现整个解析过程。
public Configuration parse () { if (parsed) { throw new BuilderException ("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once." ); } parsed = true ; parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration" )); return configuration; } private void parseConfiguration (XNode root) { try { propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties" )); Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings" )); loadCustomVfs(settings); typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases" )); pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins" )); objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory" )); objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory" )); reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory" )); settingsElement(settings); environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments" )); databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider" )); typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers" )); mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers" )); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BuilderException ("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e); } }
解析<properties>节点
XMLConfigBuilder.propertiesElement()方法会解析mybatis-config.xml配置文件中的properties节点并形成java.util.Properties对象,之后将该Properties对象设置到XPathParser和Configuration的variables字段中。在后面的解析过程中,会使用该Properties对象中的信息替换占位符。
private void propertiesElement (XNode context) throws Exception { if (context != null ) { Properties defaults = context.getChildrenAsProperties(); String resource = context.getStringAttribute("resource" ); String url = context.getStringAttribute("url" ); if (resource != null && url != null ) { throw new BuilderException ("..." ); } if (resource != null ) { defaults.putAll(Resources.getResourceAsProperties(resource)); } else if (url != null ) { defaults.putAll(Resources.getUrlAsProperties(url)); } Properties vars = configuration.getVariables(); if (vars != null ) { defaults.putAll(vars); } parser.setVariables(defaults); configuration.setVariables(defaults); } }
解析<settings>节点
XMLConfigBuilder.settingsAsProperties()方法负责解析settings节点,在settings点下的配置是MyBatis全局性的配置,它们会改变MyBatis的运行时行为,需要注意的是,在MyBatis初始化时,这些全局配置信息都会被记录到Configuration对象的对应属性中。
例如:开发人员可以通过配置autoMappingBehavior修改MyBatis是否开启自动映射的功能,具体配置如下
<settings > <!- autoMappingBehavior配置项 是决 定MyBatis是否幵 启 自动 映射功能的条 件之一 --> <setting name ="autoMappingBehavior" value ="PARTIAL" /> </settings >
在Configuration中存在一个同名的相应字段:
protected AutoMappingBehavior autoMappingBehavior = AutoMappingBehavior.PARTIAL;
settingsAsProperties()方法的解析方式与propertiesElement()方法类似,但是多了使用MetaClass检测key指定的属性在Configuration类中是否有对应setter方法的步骤。
private Properties settingsAsProperties (XNode context) { if (context == null ) { return new Properties (); } Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties(); MetaClass metaConfig = MetaClass.forClass(Configuration.class, localReflectorFactory); for (Object key : props.keySet()) { if (!metaConfig.hasSetter(String.valueOf(key))) { throw new BuilderException ("..." ); } } return props; }
解析<typeAliases>、<typeHandlers>节点
XMLConfigBuilder.typeAliasesElement()方法负责解析typeAliases节点点及其子节点,并通过TypeAliasRegistry完成别名的注册。
private void typeAliasesElement (XNode parent) { if (parent != null ) { for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) { if ("package" .equals(child.getName())) { String typeAliasPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name" ); configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAliases(typeAliasPackage); } else { String alias = child.getStringAttribute("alias" ); String type = child.getStringAttribute("type" ); try { Class<?> clazz = Resources.classForName(type); if (alias == null ) { typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(clazz); } else { typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(alias, clazz); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new BuilderException ("..." ); } } } } }
XMLConfigBuilder.typeHandlerElement()方法负责解析typeHandlers节点,并通过TypeHandlerRegistry对象完成TypeHandler的注册,该方法的实现与typeAliasesElement()方法类似。
解析<plugins>节点
插件是MyBatis提供的扩展机制之一,用户可以通过添加自定义插件在SQL语句执行过程中的某一点进行拦截。
MyBatis中的自定义插件只需实现Interceptor接口,并通过注解指定想要拦截的方法签名即可。这里分析MyBatis中如何加载和管理插件。XMLConfigBuilder.pluginElement()方法负责解析plugins节点中定义的插件,并完成实例化和配置操作。
private void pluginElement (XNode parent) throws Exception { if (parent != null ) { for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) { String interceptor = child.getStringAttribute("interceptor" ); Properties properties = child.getChildrenAsProperties(); Interceptor interceptorInstance = (Interceptor) resolveClass(interceptor).newInstance(); interceptorInstance.setProperties(properties); configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance); } } }
所有配置的Interceptor对象都是通过Configuration.interceptorChain字段(InterceptorChain类型)管理的,InterceptorChain底层使用ArrayList<Interceptor>实现。
public class InterceptorChain { private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList <Interceptor>(); public Object pluginAll (Object target) { for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) { target = interceptor.plugin(target); } return target; } public void addInterceptor (Interceptor interceptor) { interceptors.add(interceptor); } public List<Interceptor> getInterceptors () { return Collections.unmodifiableList(interceptors); } }
解析<objectFactory>节点
我们可以通过添加自定义Objectory实现类、ObjectWrapperFactory实现类以及ReflectorFactory实现类对MyBatis进行扩展。XMLConfigBuilder.objectFactoryElement()方法负责解析并实例化<objectFactory>节点指定的ObjectFactory实现类,之后将自定义的ObjectFactory对象记录到Configuration.objectFactory字段中。
private void objectFactoryElement (XNode context) throws Exception { if (context != null ) { String type = context.getStringAttribute("type" ); Properties properties = context.getChildrenAsProperties(); ObjectFactory factory = (ObjectFactory) resolveClass(type).newInstance(); factory.setProperties(properties); configuration.setObjectFactory(factory); } }
XMLConfigBuilder对<objectWrapperFactory>节点、<reflectorFactory>节点的解析与上述过程类似,最终会将解析得到的自定义对象记录到Configuration的相应字段中。
解析<environments>节点
在实际生产中,同一项目可能分为开发、测试和生产多个不同的环境,每个环境的配置可能也不尽相同。
MyBatis可以配置多个<environment>节点,每个<environment>节点对应一种环境的配置。但需要注意的是,尽管可以配置多个环境,每个SqlSessionFactory实例只能选择其一。
XMLConfigBuilder.environmentsElement()方法负责解析<environments>的相关配置,它会根据XMLConfigBuilder.environment字段值确定要使用的<environment>配置,之后创建对应的TransactionFactory和DataSource对象,并封装进Environment对象中。
private void environmentsElement (XNode context) throws Exception { if (context != null ) { if (environment == null ) { environment = context.getStringAttribute("default" ); } for (XNode child : context.getChildren()) { String id = child.getStringAttribute("id" ); if (isSpecifiedEnvironment(id)) { TransactionFactory txFactory = transactionManagerElement(child.evalNode("transactionManager" )); DataSourceFactory dsFactory = dataSourceElement(child.evalNode("dataSource" )); DataSource dataSource = dsFactory.getDataSource(); Environment.Builder environmentBuilder = new Environment .Builder(id) .transactionFactory(txFactory) .dataSource(dataSource); configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build()); } } } }
解析<databaseldProvider>节点
MyBatis不能像Hibernate那样,直接帮助开发人员屏蔽多种数据库产品在SQL语言支持方面的差异。
但是在mybatis-config.xml配置文件中,通过<databaseIdProvider>定义所有支持的数据库产品的databaseld,然后在映射配置文件中定义SQL语句节点时,通过databaseld指定该SQL语句应用的数据库产品,这样也可以实现类似的功能。
在MyBatis初始化时,会根据前面确定的DataSource确定当前使用的数据库产品,然后在解析映射配置文件时,加载不带databaseld属性和带有匹配当前数据库databaseld属性的所有SQL语句。如果同时找到带有databaseld和不带databaseld的相同语句,则后者会被舍弃,使用前者。
XMLConfigBuilder.databaseIdProviderElement()方法负责解析<databaseIdProvider>节点,并创建指定的DatabaseldProvider对象。DatabaseldProvider会返回databaseld值,MyBatis会根据databaseld选择合适的SQL进行执行。
private void databaseIdProviderElement (XNode context) throws Exception { DatabaseIdProvider databaseIdProvider = null ; if (context != null ) { String type = context.getStringAttribute("type" ); if ("VENDOR" .equals(type)) { type = "DB_VENDOR" ; } Properties properties = context.getChildrenAsProperties(); databaseIdProvider = (DatabaseIdProvider) resolveClass(type).newInstance(); databaseIdProvider.setProperties(properties); } Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment(); if (environment != null && databaseIdProvider != null ) { String databaseId = databaseIdProvider.getDatabaseId(environment.getDataSource()); configuration.setDatabaseId(databaseId); } }
MyBatis提供的DatabaseldProvider接口及其实现比较简单。
DatabaseldProvider接口的核心方法是getDatabaseId()方法,它主要负责通过给定的DataSource来查找对应的databaseld。
MyBatis提供了VendorDatabaseldProvider和DefaukDatabaseldProvider两个实现,其中DefaultDatabaseldProvider己过时。
VendorDatabaseIdProvider.getDatabaseId()方法在接收到DataSource对象时,会先解析DataSource所连接的数据库产品名称,之后根据<databaseIdProvider>节点配置的数据库产品名称与databaseld的对应关系确定最终的databaseld。
private String getDatabaseName (DataSource dataSource) throws SQLException { String productName = getDatabaseProductName(dataSource); if (this .properties != null ) { for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> property : properties.entrySet()) { if (productName.contains((String) property.getKey())) { return (String) property.getValue(); } } return null ; } return productName; } private String getDatabaseProductName (DataSource dataSource) throws SQLException { Connection con = null ; try { con = dataSource.getConnection(); DatabaseMetaData metaData = con.getMetaData(); return metaData.getDatabaseProductName(); } finally { if (con != null ) { try { con.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { } } } }
解析<mappers>节点
在MyBatis初始化时,除了加载mybatis-config.xml配置文件,还会加载全部的映射配置文件,mybatis-config.xml配置文件中的<mappers>节点会告诉MyBatis去哪些位置查找映射配置文件以及使用了配置注解标识的接口。XMLConfigBuilder.mapperElement()方法负责解析<mappers>节点,它会创建XMLMapperBuilder对象加载映射文件,如果映射配置文件存在相应的Mapper接口,也会加载相应的Mapper接口,解析其中的注解并完成向MapperRegistry的注册。
private void mapperElement (XNode parent) throws Exception { if (parent != null ) { for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) { if ("package" .equals(child.getName())) { String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name" ); configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage); } else { String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource" ); String url = child.getStringAttribute("url" ); String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class" ); if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null ) { ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource); InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder (inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments()); mapperParser.parse(); } else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null ) { ErrorContext.instance().resource(url); InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url); XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder (inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments()); mapperParser.parse(); } else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null ) { Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass); configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface); } else { throw new BuilderException ("..." ); } } } } }
XMLMapperBuilder 通过对XMLConfigBuilder.mapperElement()方法的介绍我们知道,XMLMapperBuilder负责解析映射配置文件,它继承了BaseBuilder抽象类,也是具体建造者的角色。XMLMapperBuilder.parse()方法是解析映射文件的入口。
public void parse () { if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) { configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper" )); configuration.addLoadedResource(resource); bindMapperForNamespace(); } parsePendingResultMaps(); parsePendingCacheRefs(); parsePendingStatements(); }
XMLMapperBuilder也是将每个节点的解析过程封装成了一个方法,而这些方法由XMLMapperBuilder.configurationElement()方法调用。
private void configurationElement (XNode context) { try { String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace" ); if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("" )) { throw new BuilderException ("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty" ); } builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace); cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref" )); cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache" )); parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap" )); resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap" )); sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql" )); buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete" )); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BuilderException ("..." ); } }
1. 解析<cache>节点
MyBatis拥有非常强大的二级缓存功能,该功能可以非常方便地进行配置,**MyBatis默认情**况下没有开启二级缓存,如果要为某命名空间开启二级缓存功能,则需要在相应映射配置文件中添加<cache>节点,还可以通过配置<cache>节点的相关属性,为二级缓存配置相应的特性(本质上就是添加相应的装饰器)。
XMLMapperBuilder.cacheElement()方法主要负责解析<cache>节点:
private void cacheElement (XNode context) throws Exception { if (context != null ) { String type = context.getStringAttribute("type" , "PERPETUAL" ); Class<? extends Cache > typeClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(type); String eviction = context.getStringAttribute("eviction" , "LRU" ); Class<? extends Cache > evictionClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(eviction); Long flushInterval = context.getLongAttribute("flushInterval" ); Integer size = context.getIntAttribute("size" ); boolean readWrite = !context.getBooleanAttribute("readOnly" , false ); boolean blocking = context.getBooleanAttribute("blocking" , false ); Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties(); builderAssistant.useNewCache( typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props); } }
MapperBuilderAssistant是一个辅助类,其useNewCache()方法负责创建Cache对象,并将其添加到Configuration.caches集合中保存。
Configuration中的caches字段是StrictMap<Cache>类型的字段,它记录Cache的id(默认是映射文件的namespace)与Cache对象(二级缓存)之间的对应关系。
StrictMap继承了HashMap,并在其基础上进行了少许修改,这里重点关注StrictMap.put()方法,如果检测到重复的key则抛出异常,如果没有重复的key则添加key以及value,同时会根据key产生shortKey。
public V put (String key, V value) { if (containsKey(key)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException (name + " already contains value for " + key); } if (key.contains("." )) { final String shortKey = getShortName(key); if (super .get(shortKey) == null ) { super .put(shortKey, value); } else { super .put(shortKey, (V) new Ambiguity (shortKey)); } } return super .put(key, value); }
Ambiguity是StrictMap中定义的静态内部类,它表示的是存在二义性的键值对 。Ambiguity中使用subject字段记录了存在二义性的key,并提供了相应的getter方法。
StrictMap.get()方法会检测value是否存在以及value是否为Ambiguity类型对象,如果满足这两个条件中的任意一个,则抛出异常。
public V get (Object key) { V value = super .get(key); if (value == null ) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("..." ); } if (value instanceof Ambiguity) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("..." ); } return value; }
MapperBuilderAssistant. useNewCache()方法的实现如下:
public Cache useNewCache (Class<? extends Cache> typeClass, Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass, Long flushInterval, Integer size, boolean readWrite, boolean blocking, Properties props) { Cache cache = new CacheBuilder (currentNamespace) .implementation(valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class)) .addDecorator(valueOrDefault(evictionClass, LruCache.class)) .clearInterval(flushInterval) .size(size) .readWrite(readWrite) .blocking(blocking) .properties(props) .build(); configuration.addCache(cache); currentCache = cache; return cache; }
CacheBuilder是Cache的建造者,其字段如下:
private final String id;private Class<? extends Cache > implementation;private final List<Class<? extends Cache >> decorators;private Integer size;private Long clearInterval;private boolean readWrite;private Properties properties;private boolean blocking;
CacheBuilder.build()方法,根据CacheBuilder中上述字段的值创建Cache对象并添加合适的装饰器。
public Cache build () { setDefaultImplementations(); Cache cache = newBaseCacheInstance(implementation, id); setCacheProperties(cache); if (PerpetualCache.class.equals(cache.getClass())) { for (Class<? extends Cache > decorator : decorators) { cache = newCacheDecoratorInstance(decorator, cache); setCacheProperties(cache); } cache = setStandardDecorators(cache); } else if (!LoggingCache.class.isAssignableFrom(cache.getClass())) { cache = new LoggingCache (cache); } return cache; }
CacheBuilder.setCacheProperties()方法会根据<cache>节点下配置的<property>信息,初始化Cache对象。
private void setCacheProperties (Cache cache) { if (properties != null ) { MetaObject metaCache = SystemMetaObject.forObject(cache); for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry : properties.entrySet()) { String name = (String) entry.getKey(); String value = (String) entry.getValue(); if (metaCache.hasSetter(name)) { Class<?> type = metaCache.getSetterType(name); if (String.class == type) { metaCache.setValue(name, value); } else if (int .class == type || Integer.class == type) { metaCache.setValue(name, Integer.valueOf(value)); } else if (long .class == type || Long.class == type) { metaCache.setValue(name, Long.valueOf(value)); } else if (short .class == type || Short.class == type) { metaCache.setValue(name, Short.valueOf(value)); } else if (byte .class == type || Byte.class == type) { metaCache.setValue(name, Byte.valueOf(value)); } else if (float .class == type || Float.class == type) { metaCache.setValue(name, Float.valueOf(value)); } else if (boolean .class == type || Boolean.class == type) { metaCache.setValue(name, Boolean.valueOf(value)); } else if (double .class == type || Double.class == type) { metaCache.setValue(name, Double.valueOf(value)); } else { throw new CacheException ("..." ); } } } } if (InitializingObject.class.isAssignableFrom(cache.getClass())){ try { ((InitializingObject) cache).initialize(); } catch (Exception e) { throw new CacheException ("..." , e); } } }
CacheBuilder.setStandardDecorators()方法会根据CacheBuilder中各个字段的值,为cache对象添加对应的装饰器。
private Cache setStandardDecorators (Cache cache) { try { MetaObject metaCache = SystemMetaObject.forObject(cache); if (size != null && metaCache.hasSetter("size" )) { metaCache.setValue("size" , size); } if (clearInterval != null ) { cache = new ScheduledCache (cache); ((ScheduledCache) cache).setClearInterval(clearInterval); } if (readWrite) { cache = new SerializedCache (cache); } cache = new LoggingCache (cache); cache = new SynchronizedCache (cache); if (blocking) { cache = new BlockingCache (cache); } return cache; } catch (Exception e) { throw new CacheException ("..." , e); } }
2. 解析<cache-ref>节点
XMLMapperBuilder.cacheElement()方法会为每个namespace创建一个对应的Cache对象,并在Configuration.caches集合中记录namespace与Cache对象之间的对应关系。
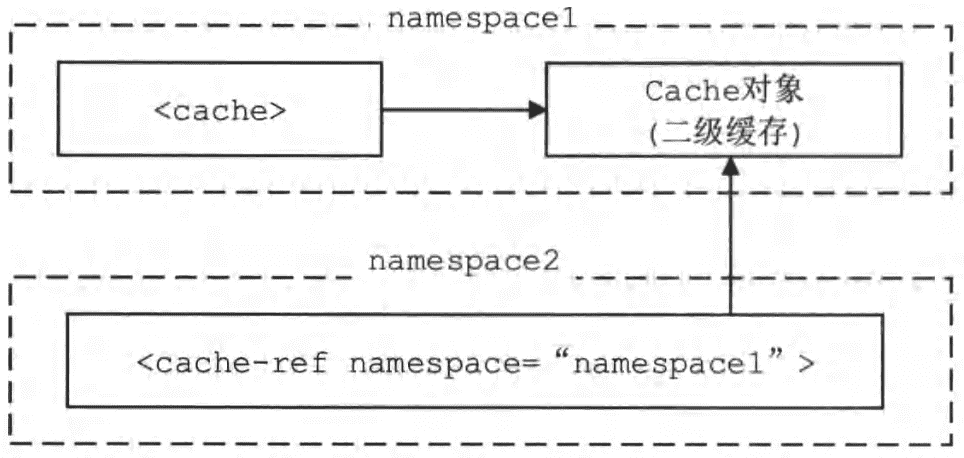
如果希望多个namespace共用同一个二级缓存,即同一个Cache对象,则可以使用<cache-ref>点进行配置。
XMLMapperBuilder.cacheReffilement()方法负责解析<cache-ref>节点。
这里首先需要了解的是Configuration.cacheRefMap集合,该集合是HashMap<String,String>类型,其中key是<cache-ref>节点所在的namespace,value是<cache-ref>节点的namespace属性所指定的namespace。
也就是说,前者共用后者的Cache对象,如下图,namespace2共用了namespace1的Cache对象。
XMLMapperBuilder.cacheReffilement():
private void cacheRefElement (XNode context) { if (context != null ) { configuration.addCacheRef( builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace(), context.getStringAttribute("namespace" )); CacheRefResolver cacheRefResolver = new CacheRefResolver ( builderAssistant, context.getStringAttribute("namespace" )); try { cacheRefResolver.resolveCacheRef(); } catch (IncompleteElementException e) { configuration.addIncompleteCacheRef(cacheRefResolver); } } }
CacheRefResolver是一个简单的Cache引用解析器,其中封装了被引用的namespace以及当前XMLMapperBuilder对应的MapperBuilderAssistant对象。
CacheRefResolver.resolveCacheRef()方法会调用MapperBuilderAssistant.useCacheRef()方法。在MapperBuilderAssistant.useCacheRef()方法中会通过namespace查找被引用的Cache对象。
public Cache useCacheRef (String namespace) { if (namespace == null ) { throw new BuilderException ("..." ); } try { unresolvedCacheRef = true ; Cache cache = configuration.getCache(namespace); if (cache == null ) { throw new IncompleteElementException ("..." ); } currentCache = cache; unresolvedCacheRef = false ; return cache; } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { throw new IncompleteElementException ("..." , e); } }
另一个需要了解的Configuration字段是incompleteCacheRefs集合,它是LinkedList<CacheRefResolver>类型,其中记录了当前解析出现异常的CacheRefResolver对象。
3. 解析<resultMap>节点
select语句查询得到的结果集是一张二维表 ,水平方向上看是一个个字段,垂直方向上看是一条条记录 。
而Java是面向对象的程序设计语言,对象是根据类定义创建的,类之间的引用关系可以认为是嵌套的结构。
在JDBC编程中,为了将结果集中的数据映射成对象,我们需要自己写代码从结果集中获取数据,然后封装成对应的对象并设置对象之间的关系,而这些都是大量的重复性代码。
为了减少这些重复的代码,MyBatis使用<resultMap>节点定义了结果集与结果对象(JavaBean对象)之间的映射规则,<resultMap>节点可以满足绝大部分的映射需求,从而减少开发人员的重复性劳动,提高开发效率。
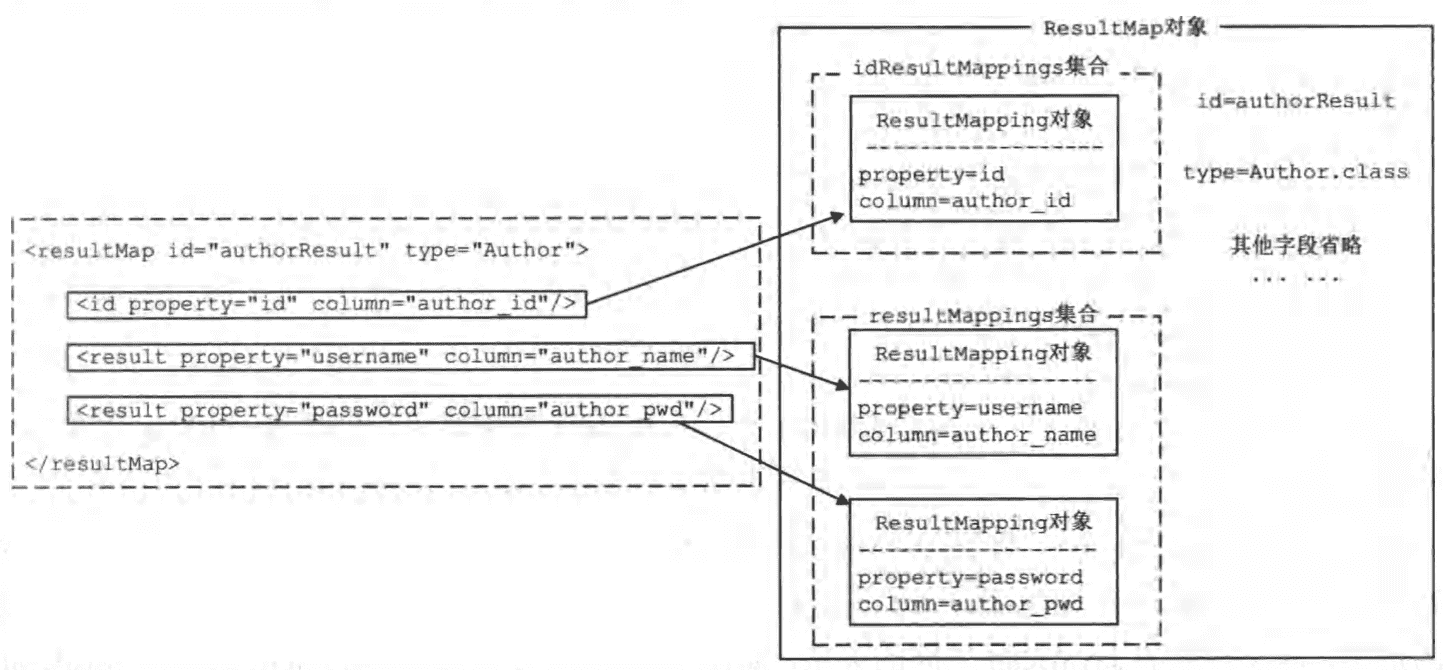
每个ResultMapping对象记录了结果集中的一列与JavaBean中一个属性之间的映射关系。<resultMap>节点下除了<discriminator>子节点的其他子节点,都会被解析成对应的ResultMapping对象。核心字段如下:
private Configuration configuration;private String property;private String column;private Class<?> javaType;private JdbcType jdbcType;private TypeHandler<?> typeHandler;private String nestedResultMapId;private String nestedQueryId;private Set<String> notNullColumns;private String columnPrefix;private List<ResultFlag> flags;private List<ResultMapping> composites;private String resultSet;private String foreignColumn;private boolean lazy;
ResultMapping中定义了一个内部Builder类,也应用了建造者模式,该Builder类主要用于数据整理和数据校验校验。
另一个比较重要的类是ResultMap,每个<resultMap>节点都会被解析成一个ResultMap对象,其中每个节点所定义的映射关系,则使用ResultMapping对象表示。
ResultMap字段定义:
private Configuration configuration;private String id;private Class<?> type;private List<ResultMapping> resultMappings;private List<ResultMapping> idResultMappings;private List<ResultMapping> constructorResultMappings;private List<ResultMapping> propertyResultMappings;private Set<String> mappedColumns;private Set<String> mappedProperties;private Discriminator discriminator;private boolean hasNestedResultMaps;private boolean hasNestedQueries;private Boolean autoMapping;
在XMLMapperBuilder中通过resultMapElements()方法解析映射配置文件中的全部<resultMap>节点,该方法会循环调用resultMapElement()方法处理每个<resultMap>节点。
private ResultMap resultMapElement (XNode resultMapNode, List<ResultMapping> additionalResultMappings) throws Exception { ErrorContext.instance().activity("processing " + resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier()); String id = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute( "id" , resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier()); String type = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute( "type" ,resultMapNode.getStringAttribute( "ofType" ,resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("resultType" , resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("javaType" )))); String extend = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("extends" ); Boolean autoMapping = resultMapNode.getBooleanAttribute("autoMapping" ); Class<?> typeClass = resolveClass(type); Discriminator discriminator = null ; List<ResultMapping> resultMappings = new ArrayList <ResultMapping>(); resultMappings.addAll(additionalResultMappings); List<XNode> resultChildren = resultMapNode.getChildren(); for (XNode resultChild : resultChildren) { if ("constructor" .equals(resultChild.getName())) { processConstructorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings); } else if ("discriminator" .equals(resultChild.getName())) { discriminator = processDiscriminatorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings); } else { List<ResultFlag> flags = new ArrayList <ResultFlag>(); if ("id" .equals(resultChild.getName())) { flags.add(ResultFlag.ID); } resultMappings.add(buildResultMappingFromContext(resultChild, typeClass, flags)); } } ResultMapResolver resultMapResolver = new ResultMapResolver (builderAssistant, id, typeClass, extend, discriminator, resultMappings, autoMapping); try { return resultMapResolver.resolve(); } catch (IncompleteElementException e) { configuration.addIncompleteResultMap(resultMapResolver); throw e; } }
在处理<resultMap>节点的过程中,该过程在执行获取到id属性和type属性之后,就会通过XMLMapperBuilder.buildResultMappingFromContext()方法为<result>节点创建对应的ResultMapping对象。
private ResultMapping buildResultMappingFromContext (XNode context, Class<?> resultType, List<ResultFlag> flags) throws Exception { String property; if (flags.contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) { property = context.getStringAttribute("name" ); } else { property = context.getStringAttribute("property" ); } String column = context.getStringAttribute("column" ); String javaType = context.getStringAttribute("javaType" ); String jdbcType = context.getStringAttribute("jdbcType" ); String nestedSelect = context.getStringAttribute("select" ); String nestedResultMap = context.getStringAttribute( "resultMap" ,processNestedResultMappings(context, Collections.<ResultMapping>emptyList())); String notNullColumn = context.getStringAttribute("notNullColumn" ); String columnPrefix = context.getStringAttribute("columnPrefix" ); String typeHandler = context.getStringAttribute("typeHandler" ); String resultSet = context.getStringAttribute("resultSet" ); String foreignColumn = context.getStringAttribute("foreignColumn" ); boolean lazy = "lazy" .equals( context.getStringAttribute("fetchType" , configuration.isLazyLoadingEnabled() ? "lazy" : "eager" )); Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveClass(javaType); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Class<? extends TypeHandler <?>> typeHandlerClass = (Class<? extends TypeHandler <?>>) resolveClass(typeHandler); JdbcType jdbcTypeEnum = resolveJdbcType(jdbcType); return builderAssistant.buildResultMapping( resultType, property, column, javaTypeClass, jdbcTypeEnum, nestedSelect, nestedResultMap, notNullColumn, columnPrefix, typeHandlerClass, flags, resultSet, foreignColumn, lazy); }
MapperBuilderAssistant.buildResultMapping()的具体实现:
public ResultMapping buildResultMapping ( Class<?> resultType, String property, String column, Class<?> javaType, JdbcType jdbcType, String nestedSelect, String nestedResultMap, String notNullColumn, String columnPrefix, Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>> typeHandler, List<ResultFlag> flags, String resultSet, String foreignColumn, boolean lazy) { Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveResultJavaType(resultType, property, javaType); TypeHandler<?> typeHandlerInstance = resolveTypeHandler(javaTypeClass, typeHandler); List<ResultMapping> composites = parseCompositeColumnName(column); return new ResultMapping .Builder(configuration, property, column, javaTypeClass) .jdbcType(jdbcType) .nestedQueryId(applyCurrentNamespace(nestedSelect, true )) .nestedResultMapId(applyCurrentNamespace(nestedResultMap, true )) .resultSet(resultSet) .typeHandler(typeHandlerInstance) .flags(flags == null ? new ArrayList <ResultFlag>() : flags) .composites(composites) .notNullColumns(parseMultipleColumnNames(notNullColumn)) .columnPrefix(columnPrefix) .foreignColumn(foreignColumn) .lazy(lazy) .build(); }
得到ResultMapping对象集合之后,会调用ResultMapResolver.resolve()方法,该方法会调用MapperBuilderAssistant.addResultMap()方法创建ResultMap对象,并将ResultMap对象添加到Configuration.resultMaps集合中保存。
public ResultMap addResultMap ( String id, Class<?> type, String extend, Discriminator discriminator, List<ResultMapping> resultMappings, Boolean autoMapping) { id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false ); extend = applyCurrentNamespace(extend, true ); if (extend != null ) { if (!configuration.hasResultMap(extend)) { throw new IncompleteElementException ("..." ); } ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(extend); List<ResultMapping> extendedResultMappings = new ArrayList <ResultMapping>(resultMap.getResultMappings()); extendedResultMappings.removeAll(resultMappings); boolean declaresConstructor = false ; for (ResultMapping resultMapping : resultMappings) { if (resultMapping.getFlags().contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) { declaresConstructor = true ; break ; } } if (declaresConstructor) { Iterator<ResultMapping> extendedResultMappingsIter = extendedResultMappings.iterator(); while (extendedResultMappingsIter.hasNext()) { if (extendedResultMappingsIter.next().getFlags().contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) { extendedResultMappingsIter.remove(); } } } resultMappings.addAll(extendedResultMappings); } ResultMap resultMap = new ResultMap .Builder(configuration, id, type, resultMappings, autoMapping) .discriminator(discriminator) .build(); configuration.addResultMap(resultMap); return resultMap; }
<constructor>节点的解析,由XMLMapperBuilder.processConstructorElement()方法完成。
private void processConstructorElement (XNode resultChild, Class<?> resultType, List<ResultMapping> resultMappings) throws Exception { List<XNode> argChildren = resultChild.getChildren(); for (XNode argChild : argChildren) { List<ResultFlag> flags = new ArrayList <ResultFlag>(); flags.add(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR); if ("idArg" .equals(argChild.getName())) { flags.add(ResultFlag.ID); } resultMappings.add(buildResultMappingFromContext(argChild, resultType, flags)); } }
之后会解析<association>节点,正如前面对XMLMapperBuilder.resultMapElement()方法的介绍,<association>节点也是在XMLMapperBuilder.buildResultMappingFromContext()方法中完成解析的。
<discriminator>节点的解析,该解析过程由XMLMapperBuilder.processDiscriminatorElement()方法完成。
private Discriminator processDiscriminatorElement (XNode context, Class<?> resultType, List<ResultMapping> resultMappings) throws Exception { String column = context.getStringAttribute("column" ); String javaType = context.getStringAttribute("javaType" ); String jdbcType = context.getStringAttribute("jdbcType" ); String typeHandler = context.getStringAttribute("typeHandler" ); Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveClass(javaType); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Class<? extends TypeHandler <?>> typeHandlerClass = (Class<? extends TypeHandler <?>>) resolveClass(typeHandler); JdbcType jdbcTypeEnum = resolveJdbcType(jdbcType); Map<String, String> discriminatorMap = new HashMap <String, String>(); for (XNode caseChild : context.getChildren()) { String value = caseChild.getStringAttribute("value" ); String resultMap = caseChild.getStringAttribute("resultMap" , processNestedResultMappings(caseChild, resultMappings)); discriminatorMap.put(value, resultMap); } return builderAssistant.buildDiscriminator(resultType, column, javaTypeClass, jdbcTypeEnum, typeHandlerClass, discriminatorMap); }
4. 解析<sql>节点
XMLMapperBuilder.sqlElement()方法负责解析映射配置文件中定义的全部<sql>节点。
private void sqlElement (List<XNode> list) throws Exception { if (configuration.getDatabaseId() != null ) { sqlElement(list, configuration.getDatabaseId()); } sqlElement(list, null ); } private void sqlElement (List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) throws Exception { for (XNode context : list) { String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId" ); String id = context.getStringAttribute("id" ); id = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(id, false ); if (databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, requiredDatabaseId)) { sqlFragments.put(id, context); } } }
XMLStatementBuilder 除了节点解析,映射文件中还有一类比较重要的节点需要解析,也就是SQL节点。SQL节点主要用于定义SQL语句,SQL节点由XMLStatementBuilder负责解析。
MyBatis使用SqlSource接口表示映射文件或注解中定义的SQL语句,但它表示的SQL语句是不能直接被数据库执行的,因为其中可能含有动态SQL语句相关的节点或是占位符等需要解析的元素。
public interface SqlSource { BoundSql getBoundSql (Object parameterObject) ; }
MyBatis使用MappedStatement表示映射配置文件中定义的SQL节点,MappedStatement包含了这些节点的很多属性。
private String resource;private Configuration configuration;private String id;private Integer fetchSize;private Integer timeout;private StatementType statementType;private ResultSetType resultSetType;private SqlSource sqlSource;private Cache cache;private ParameterMap parameterMap;private List<ResultMap> resultMaps;private boolean flushCacheRequired;private boolean useCache;private boolean resultOrdered;private SqlCommandType sqlCommandType;private KeyGenerator keyGenerator;private String[] keyProperties;private String[] keyColumns;private boolean hasNestedResultMaps;private String databaseId;private Log statementLog;private LanguageDriver lang;private String[] resultSets;
XMLStatementBuilder.parseStatementNode()方法是解析SQL节点的入口函数。
public void parseStatementNode () { String id = context.getStringAttribute("id" ); String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId" ); if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this .requiredDatabaseId)) { return ; } Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize" ); Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout" ); String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap" ); String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType" ); Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType); String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap" ); String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType" ); String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang" ); LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang); Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType); String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType" ); StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf( context.getStringAttribute("statementType" , StatementType.PREPARED.toString())); ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType); String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName(); SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH)); boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT; boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache" , !isSelect); boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache" , isSelect); boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered" , false ); XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer (configuration, builderAssistant); includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode()); processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver); SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass); String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets" ); String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty" ); String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn" ); KeyGenerator keyGenerator; String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX; keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true ); if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) { keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId); } else { keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys" , configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType)) ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE; } builderAssistant.addMappedStatement( id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType, fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered, keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets); }
1. 解析<include>节点
在解析SQL节点之前,首先通过XMLIncludeTransformer解析SQL语句中的<include>节点,该过程会将<include>节点替换成<sql>节点中定义的SQL片段,并将其中的${xxx}占位符替换成真实的参数,该解析过程在XMLIncludeTransformer.applyIncludes()方法中实现。
public void applyIncludes (Node source) { Properties variablesContext = new Properties (); Properties configurationVariables = configuration.getVariables(); if (configurationVariables != null ) { variablesContext.putAll(configurationVariables); } applyIncludes(source, variablesContext, false ); } private void applyIncludes (Node source, final Properties variablesContext, boolean included) { if (source.getNodeName().equals("include" )) { Node toInclude = findSqlFragment(getStringAttribute(source, "refid" ), variablesContext); Properties toIncludeContext = getVariablesContext(source, variablesContext); applyIncludes(toInclude, toIncludeContext, true ); if (toInclude.getOwnerDocument() != source.getOwnerDocument()) { toInclude = source.getOwnerDocument().importNode(toInclude, true ); } source.getParentNode().replaceChild(toInclude, source); while (toInclude.hasChildNodes()) { toInclude.getParentNode().insertBefore(toInclude.getFirstChild(), toInclude); } toInclude.getParentNode().removeChild(toInclude); } else if (source.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { if (included && !variablesContext.isEmpty()) { NamedNodeMap attributes = source.getAttributes(); for (int i = 0 ; i < attributes.getLength(); i++) { Node attr = attributes.item(i); attr.setNodeValue(PropertyParser.parse(attr.getNodeValue(), variablesContext)); } } NodeList children = source.getChildNodes(); for (int i = 0 ; i < children.getLength(); i++) { applyIncludes(children.item(i), variablesContext, included); } } else if (included && source.getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE && !variablesContext.isEmpty()) { source.setNodeValue(PropertyParser.parse(source.getNodeValue(), variablesContext)); } }
<inClude>节点和<sql>节点可以配合使用、多层嵌套,实现更加复杂的sql片段的重用,这样的话,解析过程就会递归更多层,流程变得更加复杂。
2. 解析<selectKey>节点
在<insert>、<update>节点中可以定义<selectKey>节点来解决主键自增问题,<selectKey>节点对应的KeyGenerator接口在后面会详细介绍,现在重点关节点的解析。
XMLStatementBuilder.processSelectKeyNodes()方法负责解析SQL节点中子节点。
private void processSelectKeyNodes (String id, Class<?> parameterTypeClass, LanguageDriver langDriver) { List<XNode> selectKeyNodes = context.evalNodes("selectKey" ); if (configuration.getDatabaseId() != null ) { parseSelectKeyNodes(id, selectKeyNodes, parameterTypeClass, langDriver, configuration.getDatabaseId()); } parseSelectKeyNodes(id, selectKeyNodes, parameterTypeClass, langDriver, null ); removeSelectKeyNodes(selectKeyNodes); }
在parseSelectKeyNodes()方法中会为<selectKey>节点生成id,检测databaseld是否匹配以及是否己经加载过相同id且databaseld不为空的<selectKey>节点,并调用parseSelectKeyNode()方法处理每个<selectKey>节点。parseSelectKeyNode()方法中,首先读取<selectKey>节点的一系列属性,然后调用LanguageDriver.createSqlSource()方法创建对应的SqlSource对象,最后创建MappedStatement对象,并添加到Configuration.mappedStatements集合中保存。
private void parseSelectKeyNode (String id, XNode nodeToHandle, Class<?> parameterTypeClass, LanguageDriver langDriver, String databaseId) { String resultType = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("resultType" ); Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType); StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf( nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("statementType" , StatementType.PREPARED.toString())); String keyProperty = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("keyProperty" ); String keyColumn = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("keyColumn" ); boolean executeBefore = "BEFORE" .equals(nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("order" , "AFTER" )); boolean useCache = false ; boolean resultOrdered = false ; KeyGenerator keyGenerator = NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE; Integer fetchSize = null ; Integer timeout = null ; boolean flushCache = false ; String parameterMap = null ; String resultMap = null ; ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = null ; SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, nodeToHandle, parameterTypeClass); SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.SELECT; builderAssistant.addMappedStatement( id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType, fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass, resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered, keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, null ); id = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(id, false ); MappedStatement keyStatement = configuration.getMappedStatement(id, false ); configuration.addKeyGenerator(id, new SelectKeyGenerator (keyStatement, executeBefore)); }
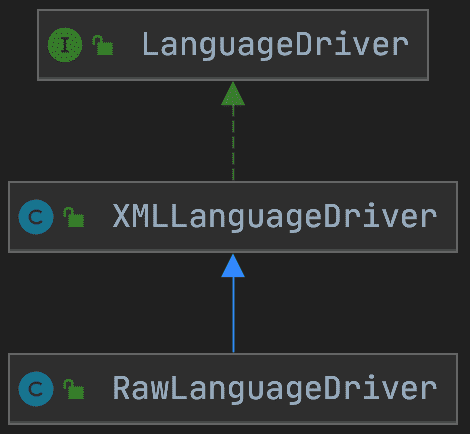
LanguageDriver接口有两个实现类。
在Configuration的构造方法中,可以看到如下代码片段,我们由此可以判断默认使用的XMLLanguageDriver实现类。
languageRegistry.setDefaultDriverClass(XMLLanguageDriver.class);
也可以提供自定义的LanguageDriver实现,并在mybatis-config.xml中通过defaultScriptingLanguage配置指定使用该自定义实现。XMLLanguageDriver.createSqlSource()方法中会创建XMLScriptBuilder对象并XMLScriptBuilder.parseScriptNode()方法创建SqlSource对象。
public SqlSource parseScriptNode () { MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(context); SqlSource sqlSource = null ; if (isDynamic) { sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource (configuration, rootSqlNode); } else { sqlSource = new RawSqlSource (configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType); } return sqlSource; }
在XMLScriptBuilder.parseDynamicTags()方法中,会遍历<selectKey>下的每个节点,如果包含任何标签节点,则认为是动态SQL语句;如果文本节点中含有${}占位符,也认为其为动态SQL语句。
protected MixedSqlNode parseDynamicTags (XNode node) { List<SqlNode> contents = new ArrayList <SqlNode>(); NodeList children = node.getNode().getChildNodes(); for (int i = 0 ; i < children.getLength(); i++) { XNode child = node.newXNode(children.item(i)); if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE || child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE) { String data = child.getStringBody("" ); TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode (data); if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) { contents.add(textSqlNode); isDynamic = true ; } else { contents.add(new StaticTextSqlNode (data)); } } else if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { String nodeName = child.getNode().getNodeName(); NodeHandler handler = nodeHandlerMap.get(nodeName); if (handler == null ) { throw new BuilderException ("Unknown element <" + nodeName + "> in SQL statement." ); } handler.handleNode(child, contents); isDynamic = true ; } } return new MixedSqlNode (contents); }
上面遇到的TextSqlNode、StaticTextSqlNode等都是SqlNode接口的实现,SqlNode接口的SQL节点类型,每个实现的具体代码后面遇到了再详细分析。
TextSqlNode.isDynamic()方法中会通过GenericTokenParser和DynamicCheckerTokenParser配合解析文本节点,并判断它是否为动态SQL。
public boolean isDynamic () { DynamicCheckerTokenParser checker = new DynamicCheckerTokenParser (); GenericTokenParser parser = createParser(checker); parser.parse(text); return checker.isDynamic(); } @Override public String handleToken (String content) { this .isDynamic = true ; return null ; }
3. 解析SQL节点
经过上述两个解析过程之后,<include>节点和<selectKey>节点己经被解析并删除掉了。XMLStatementBuilder.parseStatementNode()方法剩余的操作就是解析SQL节点。
public void parseStatementNode () { String id = context.getStringAttribute("id" ); String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId" ); if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this .requiredDatabaseId)) { return ; } Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize" ); Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout" ); String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap" ); String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType" ); Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType); String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap" ); String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType" ); String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang" ); LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang); Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType); String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType" ); StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType" , StatementType.PREPARED.toString())); ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType); String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName(); SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH)); boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT; boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache" , !isSelect); boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache" , isSelect); boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered" , false ); XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer (configuration, builderAssistant); includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode()); processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver); SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass); String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets" ); String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty" ); String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn" ); KeyGenerator keyGenerator; String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX; keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true ); if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) { keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId); } else { keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys" , configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType)) ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE; } builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType, fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass, resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered, keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets); }
绑定Mapper接口 每个映射配置文件的命名空间可以绑定一个Mapper接口,并注册到MapperRegistry中。
在XMLMapperBuilder.bindMapperForNamespace()方法中,完成了映射配置文件与对应Mapper接口的绑定。
private void bindMapperForNamespace () { String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace(); if (namespace != null ) { Class<?> boundType = null ; try { boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { } if (boundType != null ) { if (!configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) { configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace); configuration.addMapper(boundType); } } } }
在介绍MapperRegistry.addMapper()方法时,只提到了该方法会向MapperRegistry.knownMappers集合注册指定的Mapper接口,其实该方法还会创建MapperAnnotationBuilder,并调用MapperAnnotationBuilder.parse()方法解析Mapper接口中的注解信息。
public void parse () { String resource = type.toString(); if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) { loadXmlResource(); configuration.addLoadedResource(resource); assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName()); parseCache(); parseCacheRef(); Method[] methods = type.getMethods(); for (Method method : methods) { try { if (!method.isBridge()) { parseStatement(method); } } catch (IncompleteElementException e) { configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver (this , method)); } } } parsePendingMethods(); }
处理incomplete*集合 XMLMapperBuilder.configurationElement()方法解析映射配置文件时,是按照从文件头到文件尾的顺序解析的,但是有时候在解析一个节点时,会引用定义在该节点之后的、还未解析的节点,这就会导致解析失败并抛出IncompleteElementException。
根据抛出异常的节点不同,MyBatis会创建不同的*Resolver对象,并添加到Configuration的不同incomplete*集合中。
例如,
解析Mapper接口中的方法出现异常时,会创建MethodResolver对象,并将其追加到Configuration.incompleteMethods集合(LinkedList<MethodResolver>类型)中暂存;
解析<resultMap>节点时出现异常,则会将对应的ResultMapResolver对象追加到incompleteResultMaps(LinkedList<ResultMapResolver>类型)集合中暂存;
解析<cache-ref>节点时出现异常,则会将对应的CacheRefResolver对象追加到incompleteCacheRefs(LinkedList<CacheRefResolver>类型)集合中暂存;
解析SQL语句节点时出现异常,则会将对应的XMLStatementBuilder对象追加到incompleteStatements(LinkedList<XMLStatementBuilder>类型)集合中暂存。
在XMLMapperBuilder.parse()方法中可以看到,通过configurationElement()方法完了一次映射配置文件的解析后,还会调用parsePendingResultMaps()方法、parsePendingChacheRefs()方法、parsePendingStatements()方法三个parsePending*()方法处理Configuration中对应的三个incomplete*集合。所有parsePending*()方法的逻辑都是基本类似的,这里以parsePendingStatements()方法为例进行分析
private void parsePendingStatements () { Collection<XMLStatementBuilder> incompleteStatements = configuration.getIncompleteStatements(); synchronized (incompleteStatements) { Iterator<XMLStatementBuilder> iter = incompleteStatements.iterator(); while (iter.hasNext()) { try { iter.next().parseStatementNode(); iter.remove(); } catch (IncompleteElementException e) { } } } }
到此为止,MyBatis的初始化过程就全部介绍完了,其中分析了mybatis-config.xml配置文件的解析过程、映射配置文件的解析过程以及Mapper接口中相关注解的解析过程。
参考
《MyBatis技术内幕》
部分图片来源——《MyBatis技术内幕》